26 May , 18:12
6
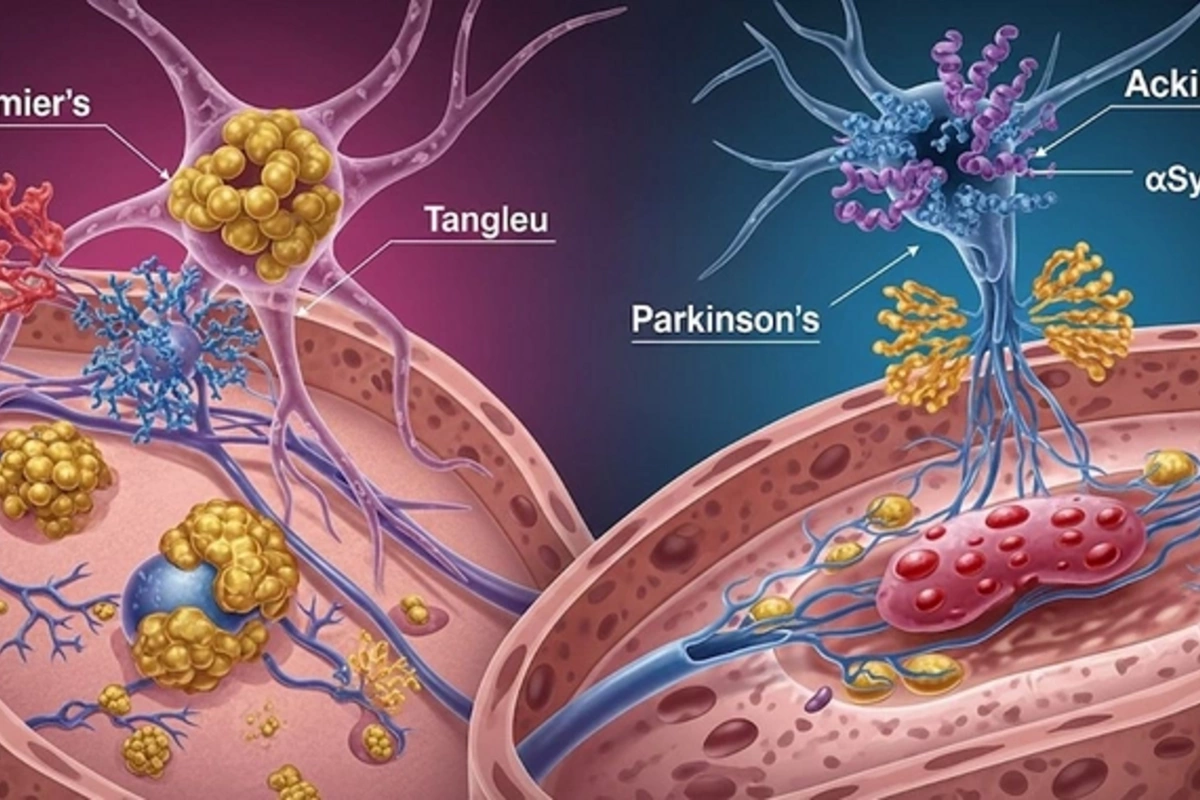
Professor Davis Joseph's sensational statement revolutionizes understanding of neurodegenerative diseases, offering a new era in the fight against Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
IMPORTANT MEDICAL DISCOVERY: INTERNATIONAL SCIENCE JOINS FORCES IN SEARCH OF A CURE
The scientific world is frozen in anticipation of revolutionary changes! Professor Davis Joseph, whose name is already resounding in scientific circles, made an astounding statement about discovering a common cause of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases – two devastating neurodegenerative conditions that until now have been studied separately. This discovery not only establishes an unexpected connection between the pathologies but also reveals a universal mechanism underlying them.
COMMON ROOT OF TWO DISEASES: HOW DOES THIS CHANGE EVERYTHING?
For decades, research on Alzheimer's and Parkinson's has proceeded along parallel courses, focusing on their specific manifestations. However, the revolutionary work of Professor Joseph and his team, published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, proved that both diseases are based on the dysfunction of the same protein, associated with the process of deamidation. This means that age-related changes disrupting the function of this protein trigger a cascade of damaged structure accumulation and subsequent neuronal death. Normalizing the level of deamidation could be the key to stopping the development of these devastating diseases.
SYNERGY OF SCIENCES: A NEW APPROACH TO UNDERSTANDING AND TREATMENT
This phenomenal discovery unites four key areas of science:
Understanding this complex relationship opens unprecedented opportunities for developing targeted treatment methods aimed not at symptoms, but at the root cause of the diseases.
FUTURE PROSPECTS: CLINICAL TRIALS AND POTENTIAL RISKS
Professor Joseph did not limit himself to theoretical calculations but proposed a specific mechanism that could become the foundation for a fundamentally new therapy. Currently, the scientific community is eagerly awaiting the start of clinical trials in humans. It should be emphasized that, like any innovative treatment, they may reveal unforeseen effects, including impacts on other protein structures or long-term consequences of 4E-BP2 regulation. Nevertheless, the potential benefits of this breakthrough could radically change the lives of millions of patients worldwide.